- cross-posted to:
- [email protected]
- cross-posted to:
- [email protected]
link to the paper https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-45347-3
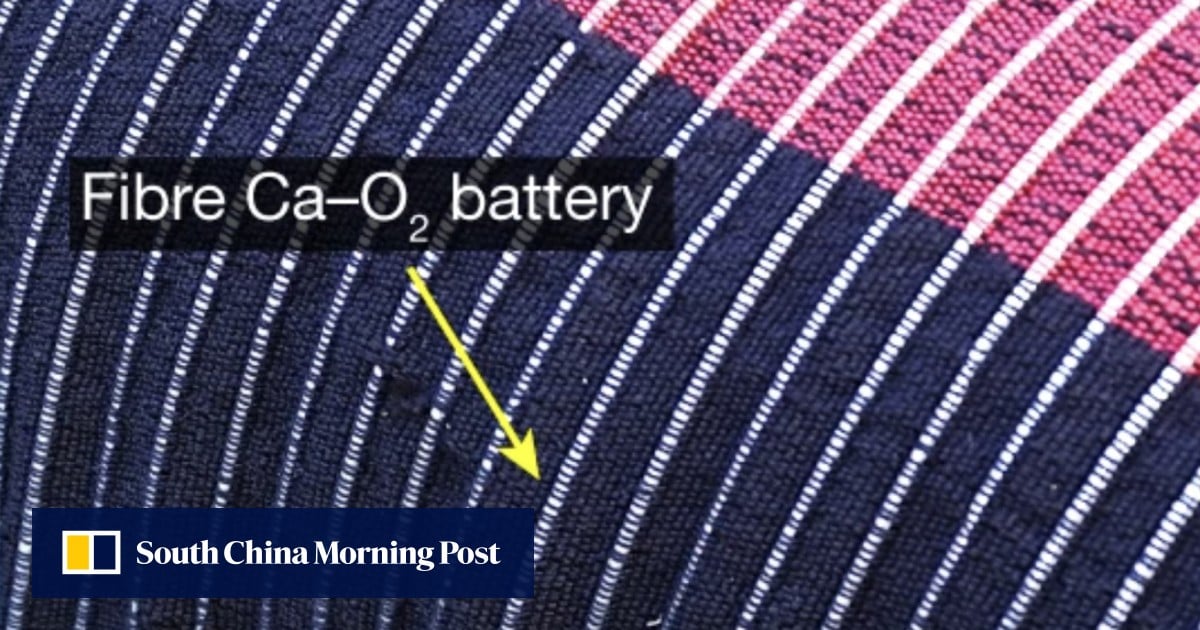
So these batteries have Calcium metal anodes and Graphite cathodes. The optimal electrolyte that they tested this with is Calcium Chloride. All of these chemicals are commonly found everywhere and not likely to create conflict minerals, which is awesome! These batteries are rechargable as well! It might be a decade or so to go from science to engineering a means to mass produce these but a great win for humanity! The only downside is that they don’t perform well in temperatures less than 0° C. Which means that some outdoor use batteries will likely still require lithium in areas with seasonal temperature drops.
The only downside is that they don’t perform well in temperatures less than 0° C
Welp, no batteries for Russia then. Guess we’re stuck with fossils
Lots of lithium is being discovered in Mexico, China, and Argintina. With climate change the thawing out polar reigions, perhaps more lithium will be discovered in Canada and Siberia. Also people in temperate climates can have devices not using lithium which means that the lithium can be used for people living in colder climates.
Yeah but all indoors uses are still on (for some reason i don’t really belive in the old Polish joke that Russians start fo feel a little chilly and close the window in bathroom at -30 C)
Can’t you put a solar panel on top and heat the batteries to keep them above 0°? I guess the problem is that you want the opposite of thermal insulation for batteries when they are working, but insulate them when it’s too cold.
Snow and lack of sun in areas where it regularly drops below zero would be an issue with that.
Snow could be melted by heating the solar panel. Unless it’s snowing constantly this could still be net positive over multiple days. This would mostly be useful for grid storage / house storage. But I could imagine an EV doing this too - a few solar panels to heat up the batteries each morning to improve efficiency. Or if it’s plugged in. It should be relatively easy and cheap to negate the problems of low temperature with 1 kW of PV for 250€, a micro controller and a temperature sensor and some resistance wire.
How does it compare to Sodium?
Not sure actually, I recall reading that sodium didn’t quite have as high energy density as lithium, and sounds like calcium might be comparable.
Wow nice, look forward to seeing what comes of it.
Battery tech is the EV battlefront.
These will not work for EV’s if they do not work bellow 0c unfortunatly.
There could be applications even in cold places. E.g. people already plug their cars in when parking outdoors in Canada in winter. Continue to do that and put a heater underneath the battery, and it’ll work. If you break down, you’re done for. But if you break down, you aren’t going anywhere, anyway.
my only worry, is there is not, atleast now, not enough public chargers. for every parking to get plugged in
Too bad that the US will not use it for another 50 years untill they “discover” it
What do you expect from a paper tiger? Where’s it going to find all that calcium without teeth or a backbone?